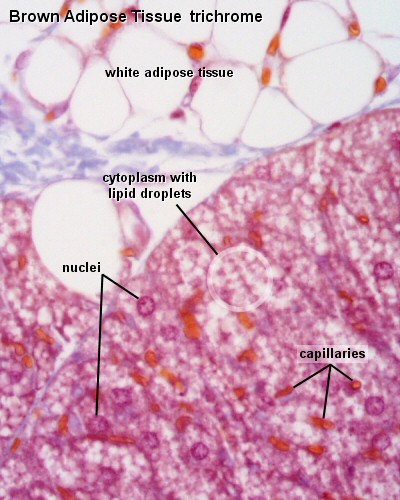
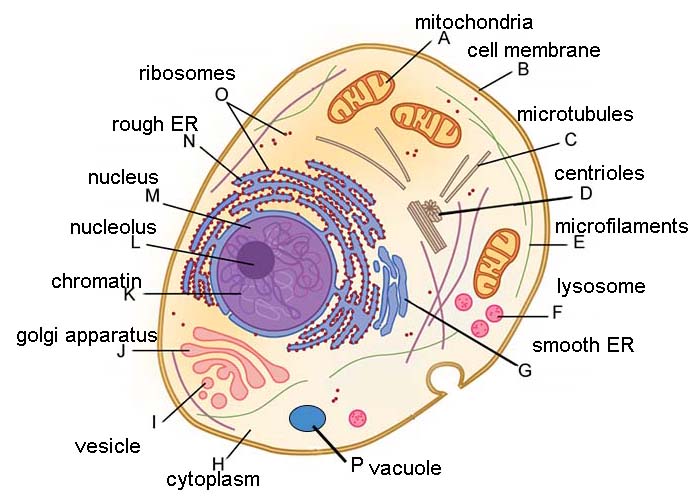
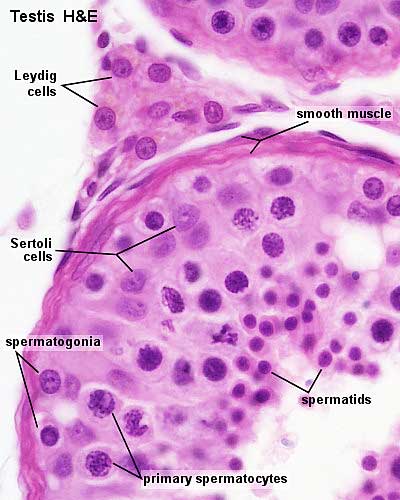
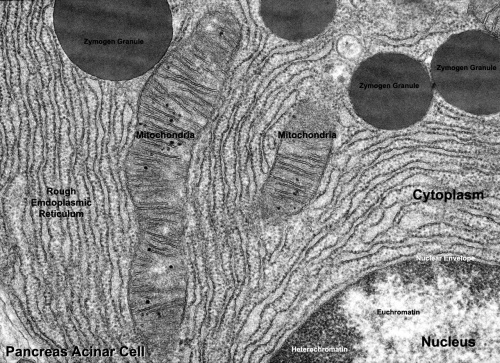
45 cell structure with labels
Cell Organelles- Definition, Structure, Functions, Diagram In a plant cell, the cell wall is made up of cellulose, hemicellulose, and proteins while in a fungal cell, it is composed of chitin. A cell wall is multilayered with a middle lamina, a primary cell wall, and a secondary cell wall. The middle lamina contains polysaccharides that provide adhesion and allow binding of the cells to one another. Unit 1 Biology and Disease Cell structure & function Practice ... cell between points P and Q. Give your answer in um. Show your working. Answer . . um (2 marks) (a) (a) (i) (ii) Name organelle Y. (1 mark) There are large numbers of organelle Y in this cell. Explain how these organelles help the cell to absorb the products of digestion. (2 marks) The diagram shows an epithelial cell from the small intestine.
Plant Cell Structure and Parts Explained With a Labeled Diagram Cell Membrane Cell membrane, also called plasma membrane, is present inside the cell wall and surrounds the cytoplasm. It connects the intracellular components (organelles and cytoplasm) with the extracellular environment, and helps in protection and transportation. The cell membrane is permeable to specific substances only. Plasmodesmata

Cell structure with labels
File:Plant cell structure svg labels.svg - Wikipedia File:Plant cell structure svg labels.svg. Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 649 × 475 pixels. Other resolutions: 320 × 234 pixels | 640 × 468 pixels | 800 × 586 pixels | 1,024 × 749 pixels | 1,280 × 937 pixels | 2,560 × 1,874 pixels. This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. Information from its description page there is shown ... Labeled cell structure? - Answers In cell F, the structure labeled Y is the nuclear membrane. It is also referred to as the nuclear envelope. Which letter correctly identifies the labeled structure within the plant cell Cell wall? Looking at the Structure of Cells in the Microscope A typical animal cell is 10–20 μm in diameter, which is about one-fifth the size of the smallest particle visible to the naked eye. It was not until good light microscopes became available in the early part of the nineteenth century that all plant and animal tissues were discovered to be aggregates of individual cells.
Cell structure with labels. Label a cell, Labeling parts of a cell, Cells Structures and Functions Start studying Label a cell, Labeling parts of a cell, Cells Structures and Functions. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. History of cell membrane theory - Wikipedia In this view, the cell was seen to be enclosed by a thin surface, the plasma membrane, and cell water and solutes such as a potassium ion existed in a physical state like that of a dilute solution. In 1889, Hamburger used hemolysis of erythrocytes to determine the permeability of various solutes. By measuring the time required for the cells to ... Cell: Structure and Functions (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion Eukaryotic Cells: 1. Eukaryotes are sophisticated cells with a well defined nucleus and cell organelles. 2. The cells are comparatively larger in size (10-100 μm). 3. Unicellular to multicellular in nature and evolved ~1 billion years ago. 4. The cell membrane is semipermeable and flexible. 5. These cells reproduce both asexually and sexually. Trypan Blue - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics In a dead cell, trypan blue passes through the porous cell membrane and enters the cytoplasm. Under light microscopy analysis, only dead cells have a blue color. Trypan blue is also used to eliminate false positives from occurring during cell counting by flow cytometry (Radu et al., 2004; Slowing et al., 2006; Trewyn et al., 2008). Fluorescein ...
Animal Cells: Labelled Diagram, Definitions, and Structure The endoplasmic reticulum (s) are organelles that create a network of membranes that transport substances around the cell. They have phospholipid bilayers. There are two types of ER: the rough ER, and the smooth ER. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is rough because it has ribosomes (which is explained below) attached to it. Cell structures- no labels Diagram | Quizlet Cell structures- no labels. STUDY. Learn. Flashcards. Write. Spell. Test. PLAY. Match. Gravity. Created by. MnmMarg PLUS. Terms in this set (12) Cell Wall. the outside of a plant cell. Cell Membrane. layer that surrounds a cell surface. Vacuole. a place where it stores food and water and other materials. Nucleus. Label the cell structure. | Study.com Label the cell structure. Cells: All living cells contain an intracellular space called the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is filled with a jelly-like fluid where many of the cells enzymatic reactions... Bacteria shapes, structure and diagram - Jotscroll The bacteria shapes, structure, and labeled diagrams are discussed below. Sizes The sizes of bacteria cells that can infect human beings range from 0.1 to 10 micrometers. Some larger types of bacteria such as the rickettsias, mycoplasmas, and chlamydias have similar sizes as the largest types of viruses, the poxviruses.
Labeled Plant Cell With Diagrams | Science Trends The Cell Wall. Let's start from the outside and work our way inwards. To start with, the entire cell is enveloped by a rigid structure called the cell wall. The cell wall's function is to give protection to the cell and to support it. The cell wall must be both permeable yet rigid. PDF Human Cell Diagram, Parts, Pictures, Structure and Functions The endoplasmic reticulum(ER) is a membranous structure that contains a network of tubules and vesicles. Its structure is such that substances can move through it and be kept in isolation from the rest of the cell until the manufacturing processes conducted within are completed. Cell Structure | Thermo Fisher Scientific - US Cell Structure. Organelle structures play a critical role in cellular function, and the detection of specific cell structures is key in fluorescence imaging of cells and tissue. Cell structure labels can be a counterstain method to identify the location of specific proteins and targets of interest within the cell. Label Cell Parts | Plant & Animal Cell Activity | StoryboardThat Create a cell diagram with each part of plant and animal cells labeled. Include descriptions of what each organelle does. Click "Start Assignment". Find diagrams of a plant and an animal cell in the Science tab. Using arrows and Textables, label each part of the cell and describe its function.
PDF Bio Cell Structure and Function Chart and Review The cell theory has three principles. •All organisms are made of cells. 3.1 Cell Theory •All existing cells are produced by other living cells. •The cell is the most basic unit of life. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles; prokaryotic cells do not. All cells share certain characteristics. •Cells tend to be microscopic.
Cell Structure and Function Quiz - Mr. Skerrett Cell Structure and Function Quiz. Cell Structure and Function Quiz Identify the following : Label 1 is. -- Choose an answer -- Cell Membrane Unit Membrane Cell Wall Cytoplasm. Label 2 is. -- Choose an answer -- Lysosome Golgi Apparatus Smooth ER Rough ER. Label 3 is.
Animal Cell Diagram with Label and Explanation: Cell Structure, Functions Animal cell is a typical Eukaryotic cell enclosed by a plasma membrane containing nucleus and organelles which lack cell walls, unlike all other Eukaryotic cells. The typical cell ranges in size between 1-100 micrometers. The lack of cell walls enabled the animal cells to develop a greater diversity of cell types.
Cell - Label | Cell Structure Quiz - Quizizz answer choices Cell wall Cell membrane Nuclear membrane Gatekeeper Question 3 30 seconds Q. Label #5 answer choices Nucleus Nucleolus Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria Question 4 30 seconds Q. Label #6 answer choices Mitochondria Chromatins Golgi Bodies Ribosomes Question 5 30 seconds Q. Label #7 answer choices Lysosomes Golgi Bodies Nucleus
Plant Cell - Definition, Structure, Function, Diagram & Types It is a rigid layer which is composed of polysaccharides cellulose, pectin and hemicellulose. It is located outside the cell membrane. It also comprises glycoproteins and polymers such as lignin, cutin, or suberin. The primary function of the cell wall is to protect and provide structural support to the cell.
Human Cell Diagram, Parts, Pictures, Structure and Functions Human Cell Diagram, Parts, Pictures, Structure and Functions. The cell is the basic functional in a human meaning that it is a self-contained and fully operational living entity. Humans are multicellular organisms with various different types of cells that work together to sustain life. Other non-cellular components in the body include water ...
A Labeled Diagram of the Plant Cell and Functions of its Organelles A Labeled Diagram of the Plant Cell and Functions of its Organelles. We are aware that all life stems from a single cell, and that the cell is the most basic unit of all living organisms. ... It is a membrane-bound structure that contains the cells hereditary information. Function: Controls expression and transcription of the gene. Nucleolus.
Plant Cells: Labelled Diagram, Definitions, and Structure The cell wall is made of cellulose and lignin, which are strong and tough compounds. Plant Cells Labelled Plastids and Chloroplasts Plants make their own food through photosynthesis. Plant cells have plastids, which animal cells don't. Plastids are organelles used to make and store needed compounds. Chloroplasts are the most important of plastids.
Cell Membrane 3 D Structure Labeled : Functions and Diagram Cell Membrane 3 D Structure.It protects the integrity of the cell along with supporting the cell and helping to maintain the cell's shape. The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is a thin layer that surrounds the cytoplasm of all prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including plant and animal cells.
Plant Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram Plants cells have DNA that helps in making new cells, hence enhancing the growth of the plant. the DNA is enclosed within the nucleus, an enveloped membrane structure at the center of the cell. The plant cell also has several cell organelle structures performing a variety of functions to maintain cellular metabolisms, growth, and development.

Chapter 8 Cell - Structure And Functions - NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science CBSE - TopperLearning
Cell Worksheets | Plant and Animal Cells Label the Parts of a Plant Cell This follow-up activity pdf worksheet on labeling the parts of a plant cell assists in testing the knowledge of 5th grade and 6th grade students. The students are expected to identify the 10 parts marked and name them with words from the word bank. Name the Parts of a Plant Cell
Animal Cell - Structure, Function, Diagram and Types The cell is the structural and functional unit of life. These cells differ in their shapes, sizes and their structure as they have to fulfil specific functions. Plant cells and animal cells share some common features as both are eukaryotic cells. However, they differ as animals need to adapt to a more active and non-sedentary lifestyle.
Cells and cell structure quiz questions - Footprints-Science ... Cell structure Cell division Transport in cells Digestive system Heart and blood Health issues Plant tissues, organs and systems Communicable diseases Drugs Plant disease Photosynthesis Respiration Homeostasis Nervous system Hormones Reproduction Variation and Evolution Ecosystems Biodiversity Trophic levels Food production States of matter Elements, compounds and mixtures Atomic structure The ...
Plant and Animal Cell: Labeled Diagram, Structure, Function - Embibe Both plant and animal cells have similar types of architecture. They are made up of cell boundaries, cytoplasm, nucleus and several cellular organelles. Structure. Description and function. Cell Wall. 1. Non-living, rigid, outer boundary. 2. Made up of cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin, lignin, etc.




Post a Comment for "45 cell structure with labels"