42 dna structure and labels
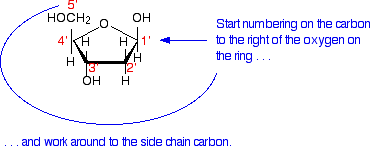
DNA Structure And Function, Definition, Examples And Diagrams DNA Structure and Function DNA is made of nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed of sugar group, phosphate group and a nitrogen base. Sugar group The repeated unit of sugar and phosphate group is the backbone of DNA. From the abbreviation of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (Ribonucleic acid) we can get the name of sugar group. DNA: Structure, Forms and Functions (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion DNA contains β D 2′-deoxyribose sugar. It is a five-carbon sugar; hence it is a pentose sugar. Since one oxygen atom at the 2′ carbon is missing it get its name 2′-deoxy. The 2′- deoxy-containing backbone is more resistant to hydrolysis than the riboform. D-ribose does not mean dextrorotary ribose.
DNA Structure and Function | Biology I Laboratory Manual - Lumen Learning DNA: 3′ AG C C G T A GAA T T 5′ Using this strand of DNA as a template, draw a picture of the complete DNA molecule. Include all parts of the DNA molecule. You do not need to draw your molecule with atomic accuracy. Now draw a complete picture of the mRNA strand that will be made from this DNA. Label the 5′ and 3′ ends of your mRNA ...
Dna structure and labels
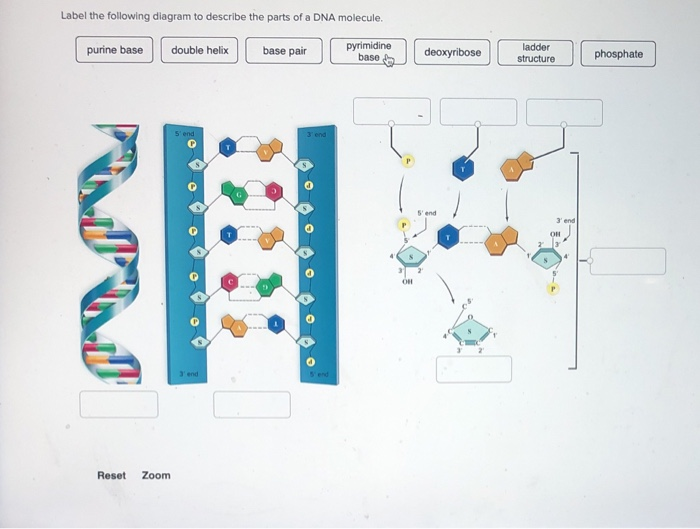
Structure of DNA: Primary and secondary structure - The Fact Factor The primary structure of DNA is simply the sequence of nucleotides. The sugar-phosphate chain is called the DNA backbone, and it is constant throughout the entire DNA molecule. The variable portion of DNA is the sequence of nitrogenous bases. The phosphate groups link the 3rd carbon of one sugar (of deoxyribose or ribose) to the 5th carbon of ... DNA function & structure (with diagram) (article) | Khan Academy DNA structure and function DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes. Health News | Latest Medical, Nutrition, Fitness News - ABC News - ABC News 6.10.2022 · Get the latest health news, diet & fitness information, medical research, health care trends and health issues that affect you and your family on ABCNews.com
Dna structure and labels. Technology and Science News - ABC News 17.10.2022 · Get the latest science news and technology news, read tech reviews and more at ABC News. PDF DNA Structure: A-, B- and Z-DNA Helix Families - Boston University structure is known as B-DNA, and represents an average conformation of DNA, based on fibre diffraction studies. However, this average shape of DNA is very unlikely to exist within the cells of living organisms, for several reasons. First, there is simply not enough room for the DNA to be stretched out in a perfect, linear B-DNA conformation. DNA Structure with Labels - Rae Rocks Teaching Help your students finally understand DNA structure with labels to help them along the way. Nearly 65% of people are visual learners which make graphics key to engaging students. This no-prep lesson provides all the basics you need to provide students to grasp the structure of DNA. $ 4.99 Add to cart DNA Structure with Labels Quinolone antibiotic - Wikipedia A quinolone antibiotic is a member of a large group of broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-quinolone. They are used in human and veterinary medicine to treat bacterial infections, as well as in animal husbandry, specifically poultry production.. Nearly all quinolone antibiotics in use are fluoroquinolones, which contain …
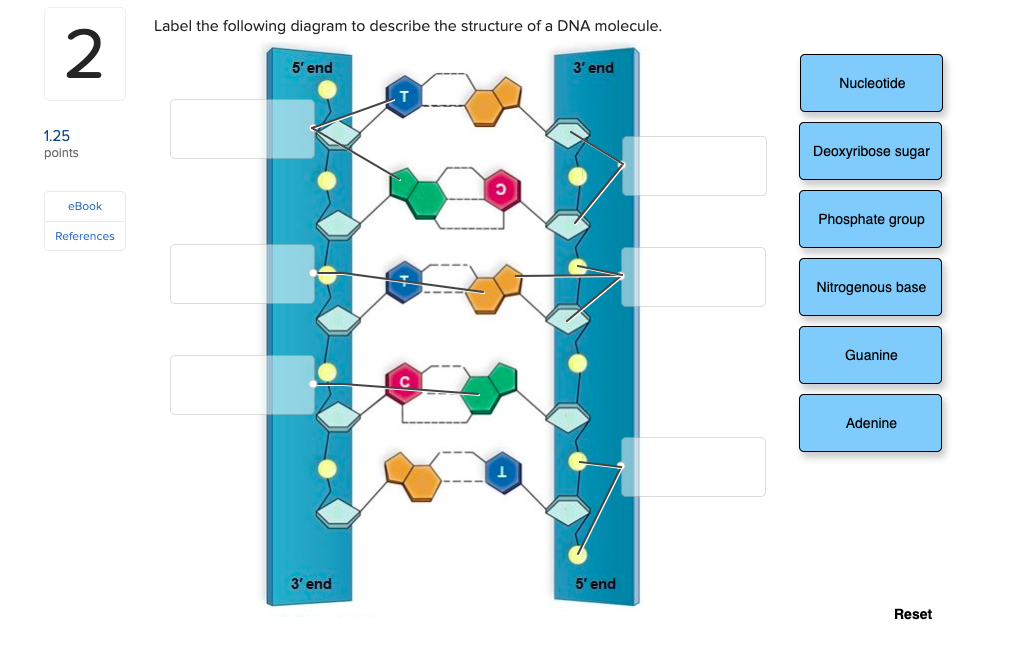
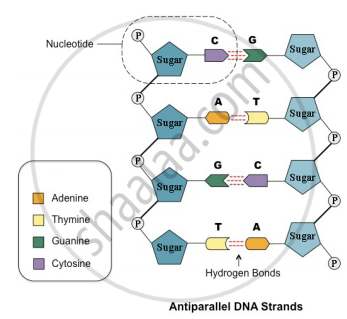
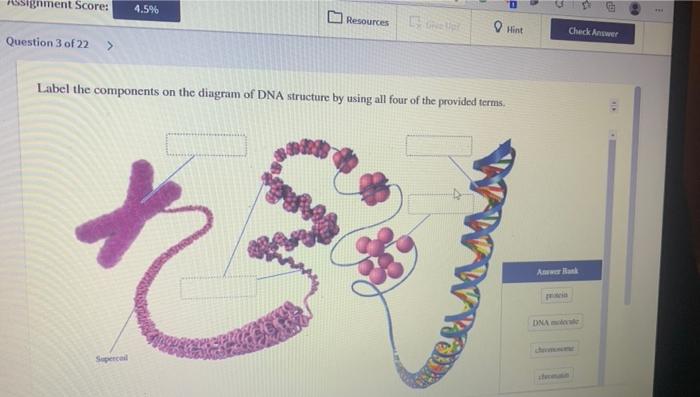
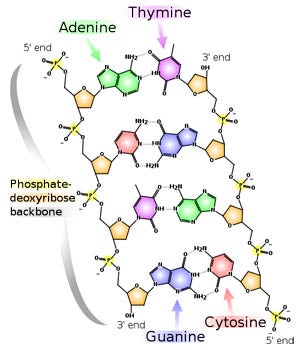
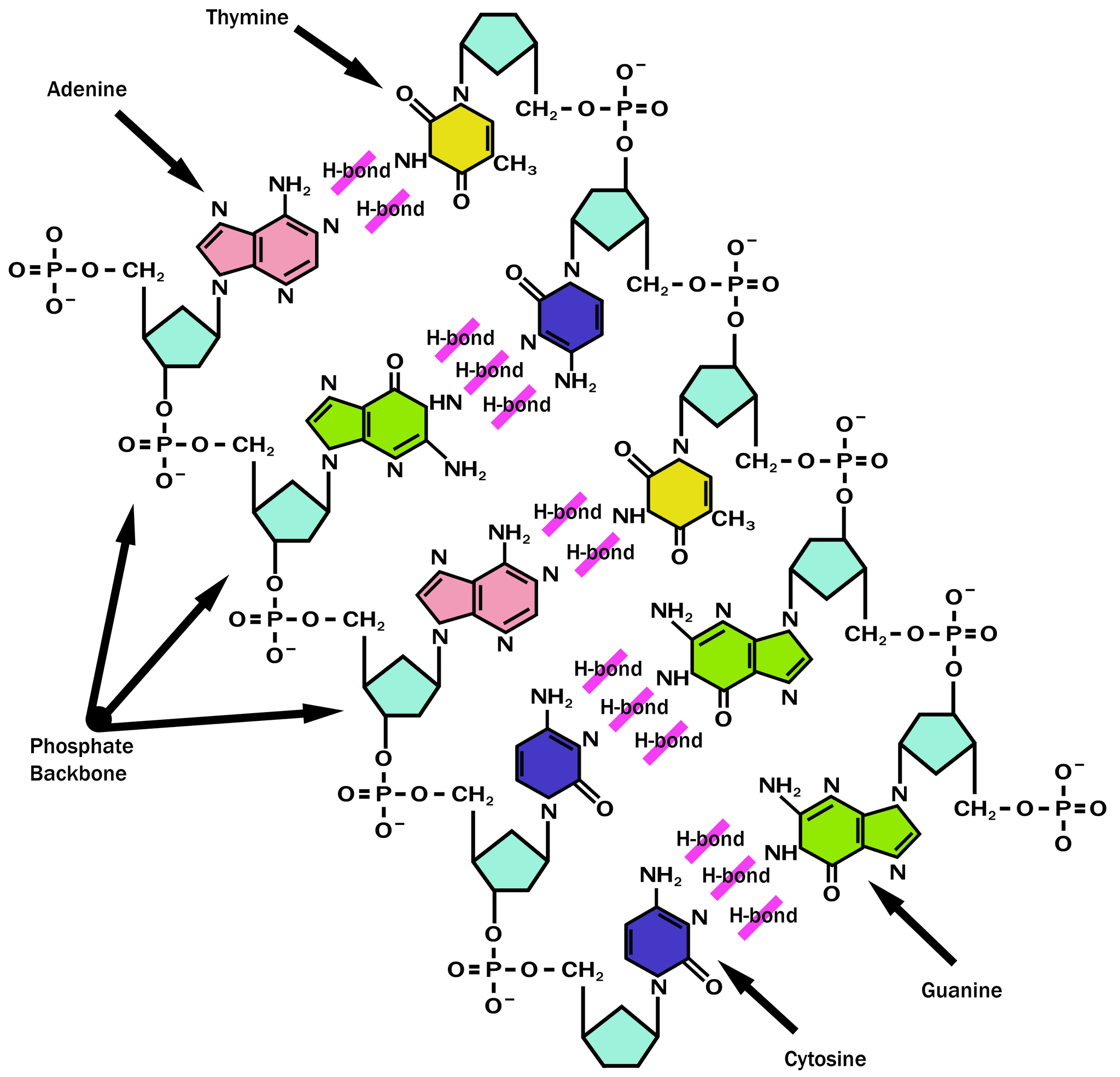
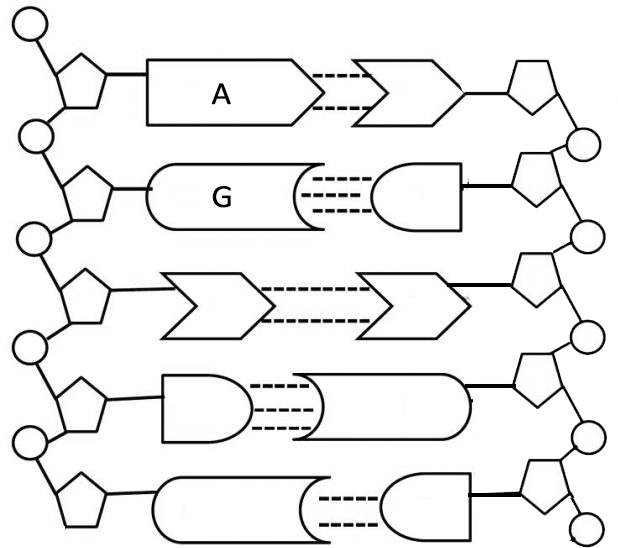
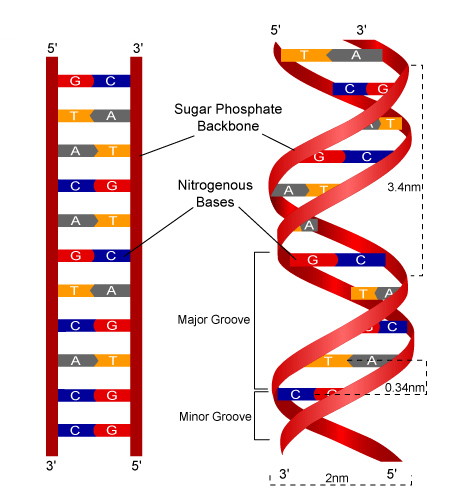
DNA and RNA Probe Labeling | Radiolabeled Nucleotides - PerkinElmer DNA polymerase I is then used to replace the nicked sites, elongating the 3' hydroxyl terminus, removing nucleotides by 5'-3' exonuclease activity, and replacing with dNTPs. To radioactively label a DNA fragment for use as a probe, one of the incorporated nucleotides provided in the reaction is radiolabeled on the alpha phosphate position. The ... DNA - Wikipedia DNA is a long polymer made from repeating units called nucleotides, each of which is usually symbolized by a single letter: either A, T, C, or G. The structure of DNA is dynamic along its length, being capable of coiling into tight loops and other shapes. In all species it is composed of two helical chains, bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. ... DNA Molecule Label Diagram | Quizlet A type of sugar on the side of a DNA molecule. Phosphate. Molecule found on the side of a DNA molecule. Double Helix. two strands of nucleotides wound about each other; structure of DNA. Thymine. the nucleotide that hydrogen bonds with the nucleotide adenine in DNA. Adenine. 9.1 The Structure of DNA - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian Edition A DNA molecule is composed of two strands. Each strand is composed of nucleotides bonded together covalently between the phosphate group of one and the deoxyribose sugar of the next. From this backbone extend the bases. The bases of one strand bond to the bases of the second strand with hydrogen bonds.
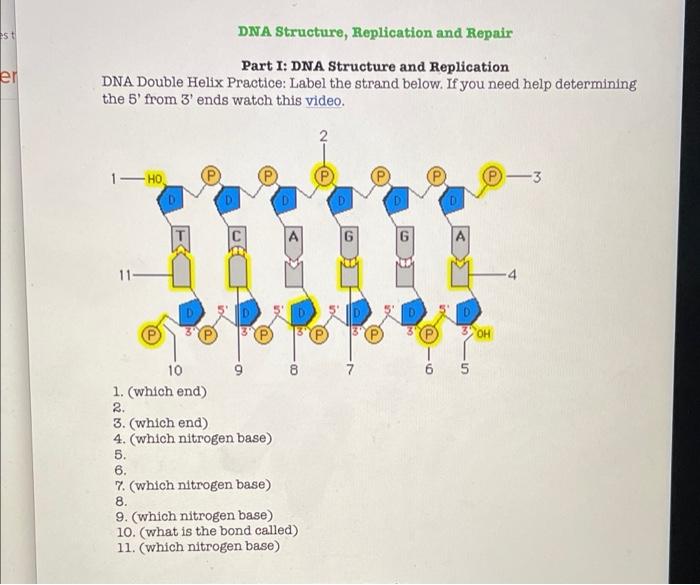
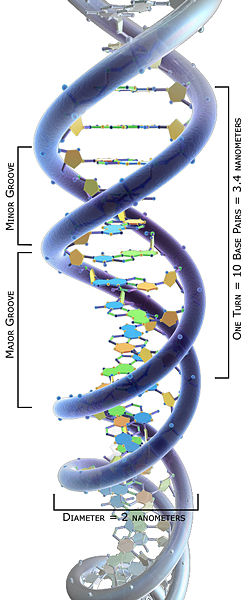
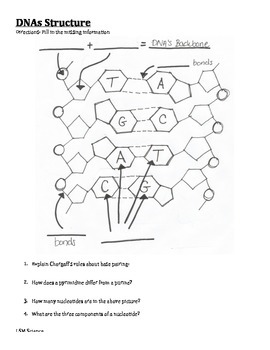
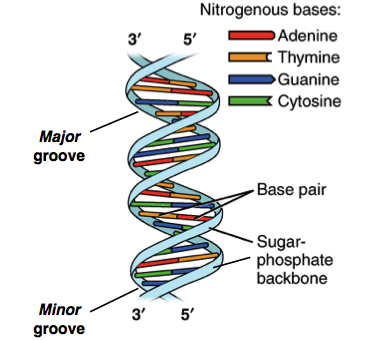
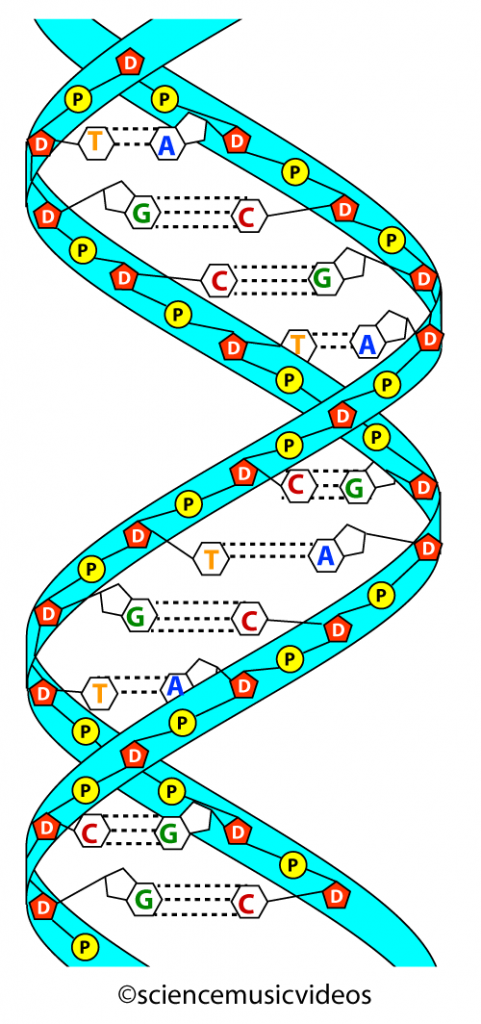
DNA structure and replication review (article) | Khan Academy DNA replication is semi-conservative. This means that each of the two strands in double-stranded DNA acts as a template to produce two new strands. Replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle explained by Chargaff's rules: adenine (A) always bonds with thymine (T) and cytosine (C) always bonds with guanine (G). Domain Name System - Wikipedia The Domain Name System (DNS) is the hierarchical and decentralized naming system used to identify computers reachable through the Internet or other Internet Protocol (IP) networks. The resource records contained in the DNS associate domain names with other forms of information. These are most commonly used to map human-friendly domain names to the numerical IP … DNA Structure | Biology Dictionary The base pairs of DNA are: Adenine-thymine Guanine-cytosine Base pairs in DNA The two strands of the double helix run in opposite directions to one another, meaning that the 5' end of one strand faces the 3' end of the other. This is called the antiparallel orientation, and it is essential for successful DNA replication. Folding DNA to create nanoscale shapes and patterns | Nature 16.3.2006 · The first step is to build a geometric model of a DNA structure that will approximate the desired shape. Figure 1a shows an example shape (outlined in red) that is 33 nm wide and 35 nm tall.
DNA Structure - YouTube Learn about the structure of DNA and how to recognize all the parts in this video!
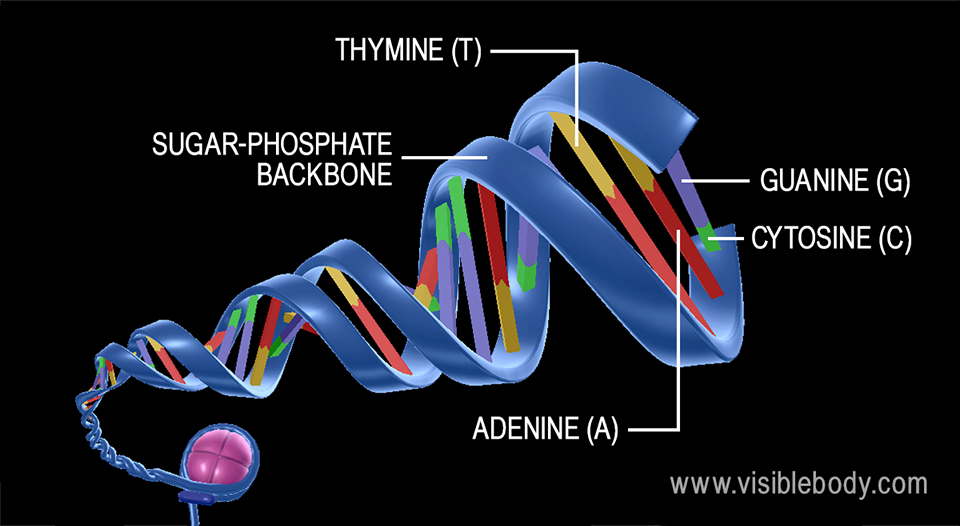
Nucleotide Structure: DNA Diagram | Science Trends DNA is known for its double helix structure. The double helix is two strands that are intertwined with one another thanks to the complementary bases. RNA is a single-stranded molecule by contrast. The double helix form of DNA helps keep the genetic code intact.
DNA structure - Structure of DNA - Higher Biology Revision - BBC DNA is the molecule that holds the instructions for growth and development in every living thing. Its structure is described as a double-stranded helix held together by complementary base...
DNA Structure - Visible Body DNA A molecule of DNA has two strands, composed of nucleotides, that form a double helix shape. 2. Each DNA strand is composed of nucleotides—units made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. Each strand of DNA is a polynucleotide composed of units called nucleotides.
Molecular models of DNA - Wikipedia From the very early stages of structural studies of DNA by X-ray diffraction and biochemical means, molecular models such as the Watson-Crick nucleic acid double helix model were successfully employed to solve the 'puzzle' of DNA structure, and also find how the latter relates to its key functions in living cells. The first high quality X-ray diffraction patterns of A-DNA were …
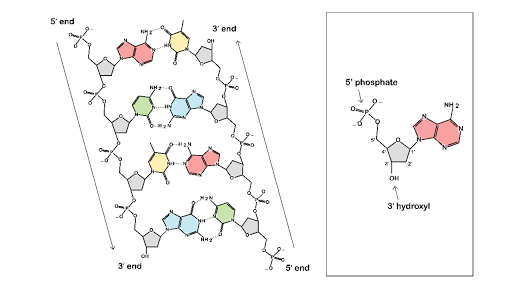
The Structure and Function of DNA - Molecular Biology of the Cell ... A DNA Molecule Consists of Two Complementary Chains of Nucleotides A DNA molecule consists of two long polynucleotide chains composed of four types of nucleotide subunits. Each of these chains is known as a DNA chain, or a DNA strand. Hydrogen bonds between the base portions of the nucleotides hold the two chains together ( Figure 4-3 ).
What Is DNA? Summary, Structure, and Importance - Healthline The two strands of DNA form a 3-D structure called a double helix. When illustrated, DNA looks like a spiral ladder in which the base pairs are the rungs, and the sugar-phosphate backbones are the ...
Open Access | Open Access Publications » A complete version of the work and all supplemental materials, including a copy of the permission as stated above, in a suitable standard electronic format is deposited immediately upon initial publication in at least one online repository that is supported by an academic institution, scholarly society, government agency, or other well-established organization that …
Dna Model: Types of DNA, Levels, Structure, Diagram - Embibe DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the largest macromolecule or biopolymer that is made up of small monomeric units called nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds. DNA carries the genetic instructions for the functioning, development, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses.
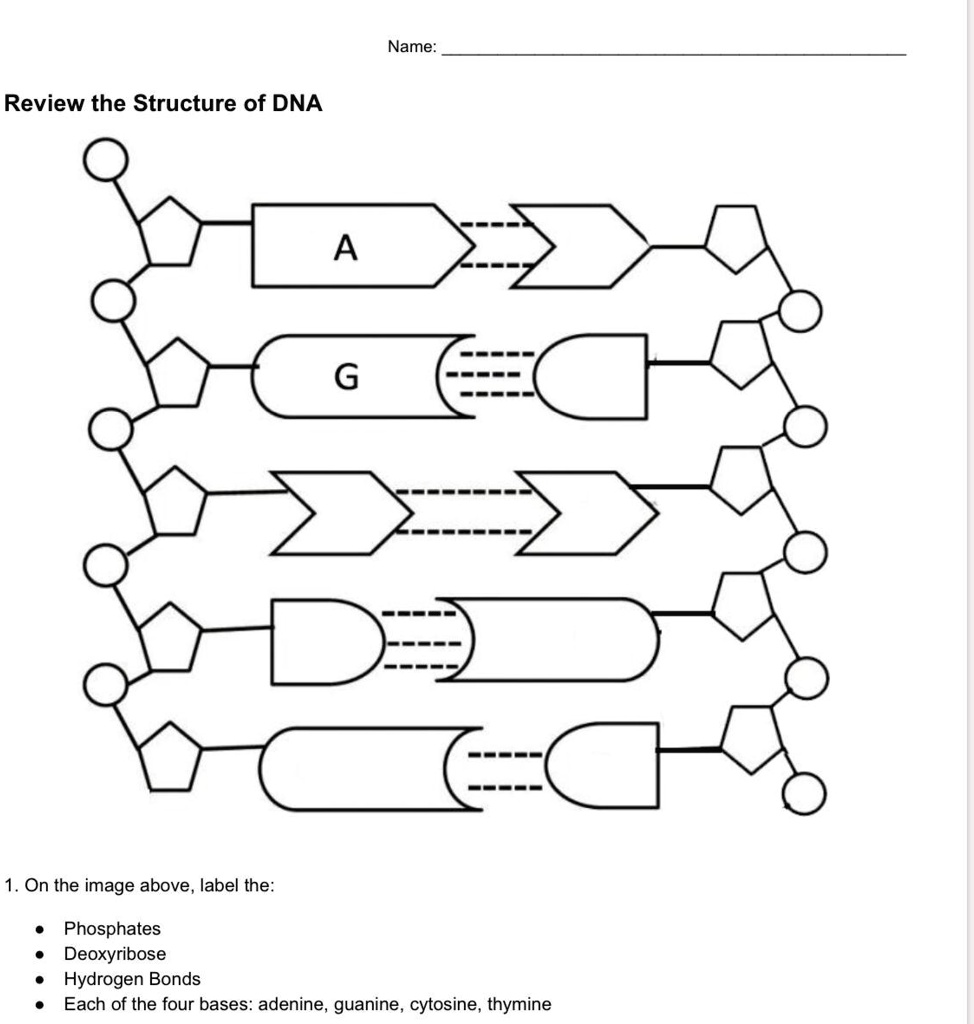
The Structure of DNA - Steward Observatory Each nucleotide is itself make of three subunits: A five carbon sugar called deoxyribose (Labeled S) A phosphate group (a phosphorous atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms.) (Labeled P) And one of four nitrogen-containing molecules called nucleotides . (Labeled A, T, C, or G)
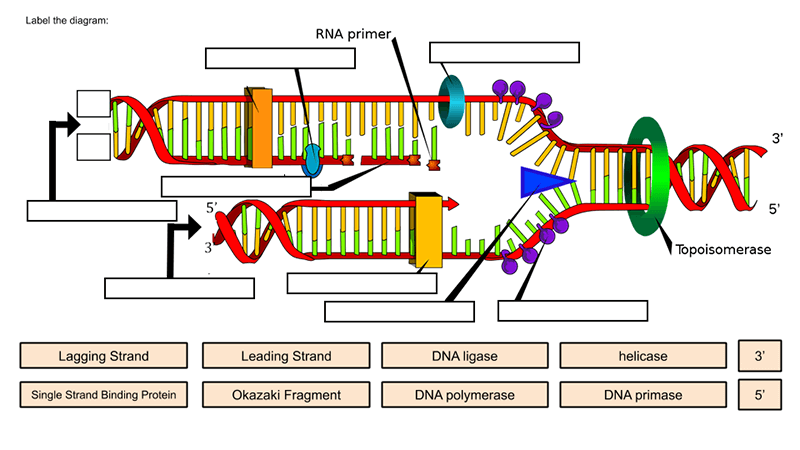
DNA ligase - Wikipedia DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (EC 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond.It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms, but some forms (such as DNA ligase IV) may specifically repair double-strand breaks (i.e. a break in both complementary strands of DNA).
3.3.5 Draw a simple diagram of DNA structure - YouTube 3.3.5 Draw and label a simple diagram of the molecular structure of DNA. Here I demonstrate drawing the structure of DNA. You don't need to be an artist, its relative positions of the...
DNA Structure (Interactive Tutorial) - learn-biology DNA is composed of two intertwined strands of nucleotides. Let's look at how each strand forms. 1. The nucleotides connect through sugar-phosphate bonds: a covalent bond between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the deoxyribose of the next nucleotide. 2.
Structure Of DNA | Function, Summary, Diagram & Model - A Level Biology It is called double helix because, in the three-dimensional model, DNA molecule was seen to have a spiral or helical structure made up of two polynucleotide chains. This helical structure was made when the two polynucleotide chains are wound around each other. 3. The polynucleotide chains are coiled anti-parallel.
What Is DNA?- Meaning, DNA Types, Structure and Functions - Byju's The DNA molecule consists of 4 nitrogen bases, namely adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and Guanine (G), which ultimately form the structure of a nucleotide. The A and G are purines, and the C and T are pyrimidines. The two strands of DNA run in opposite directions.
dna-labeling | NEB - New England Biolabs DNA Labeling. Nucleic acids are readily labeled with tags that facilitate detection or purification. A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate nucleic acids labeled with radioactive phosphates, fluorophores, or nucleotides modified with biotin or digoxygenin for example. Nucleic acids may be labeled at their 5´ end ...
DNA explained: Structure, function, and impact on health DNA is a molecule found in most cells holding each person's unique genetic code. It is responsible for coding proteins, which are essential to the growth and development of cells. Chromosomes ...
Course Help Online - Have your academic paper written by a … All our academic papers are written from scratch. All our clients are privileged to have all their academic papers written from scratch. These papers are also written according to your lecturer’s instructions and thus minimizing any chances of plagiarism.
Somalis - Wikipedia Samaale, the oldest common ancestor of several Somali clans, is generally regarded as the source of the ethnonym Somali.One other theory is that the name is held to be derived from the words soo and maal, which together mean "go and milk".This interpretation differs depending on region with northern Somalis imply it refers to go and milk in regards to the camel's milk, …
DNA Structure Labeling Diagram | Quizlet double helix. the spiral-staircase structure characteristic of the DNA molecule. nitrogen base. a subunit of a nucleotide in DNA and RNA. pyrimidine. a nitrogen base that has a single-ring structure (thymine, cytosine, and uracil) purine. a nitrogen base that has a double-ring structure (adenine and guanine) thymine.
DNA - structure - chemguide The final piece that we need to add to this structure before we can build a DNA strand is one of four complicated organic bases. In DNA, these bases are cytosine (C), thymine (T), adenine (A) and guanine (G). Note: These are called "bases" because that is exactly what they are in chemical terms.
Health News | Latest Medical, Nutrition, Fitness News - ABC News - ABC News 6.10.2022 · Get the latest health news, diet & fitness information, medical research, health care trends and health issues that affect you and your family on ABCNews.com
DNA function & structure (with diagram) (article) | Khan Academy DNA structure and function DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes.
Structure of DNA: Primary and secondary structure - The Fact Factor The primary structure of DNA is simply the sequence of nucleotides. The sugar-phosphate chain is called the DNA backbone, and it is constant throughout the entire DNA molecule. The variable portion of DNA is the sequence of nitrogenous bases. The phosphate groups link the 3rd carbon of one sugar (of deoxyribose or ribose) to the 5th carbon of ...


















Post a Comment for "42 dna structure and labels"